-
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Basics of Mandatory Medicare Coverage
- The Importance of Medicare Coverage: Is it Really Mandatory?
- Exploring the Legal Requirements of Medicare Coverage
- Medicare Coverage: Who is Eligible and Why it Matters
- The Pros and Cons of Mandatory Medicare Coverage
- Navigating the Different Parts of Medicare: A Mandatory Guide
- Medicare Coverage: What Happens if You Don’t Enroll?
- The Financial Implications of Mandatory Medicare Coverage
- Medicare Coverage: How it Affects Your Healthcare Options
- Demystifying the Myths: Debunking Misconceptions about Mandatory Medicare Coverage
- Conclusion
Is Medicare coverage mandatory?
Introduction
Medicare coverage is not mandatory for all individuals. However, it is mandatory for certain groups of people, such as those who are 65 years or older and eligible for Social Security benefits. Additionally, individuals under 65 with certain disabilities or end-stage renal disease may also be required to enroll in Medicare.
Find Medicare Plans in 3 Easy Steps
We can help get up to $0 monthly premium Medicare plans
Understanding the Basics of Mandatory Medicare Coverage
Is Medicare coverage mandatory? This is a question that many people have when it comes to understanding the basics of Medicare. In order to answer this question, it is important to have a clear understanding of what Medicare is and how it works.
Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for individuals who are 65 years of age or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. It is divided into several parts, including Part A, which covers hospital stays, and Part B, which covers doctor visits and other outpatient services. There is also Part C, which is known as Medicare Advantage, and Part D, which covers prescription drugs.
While Medicare is available to eligible individuals, it is not mandatory. However, there are certain circumstances in which individuals may be required to enroll in Medicare. For example, if you are receiving Social Security benefits, you will be automatically enrolled in Medicare Parts A and B when you turn 65. This is because Medicare is closely linked to Social Security, and the two programs work together to provide health insurance coverage for older Americans.
In addition, if you are not receiving Social Security benefits but are eligible for Medicare, you may still be required to enroll in Medicare Part A. This is because Part A helps to cover the cost of hospital stays, and it is funded through payroll taxes that individuals pay throughout their working lives. If you do not enroll in Part A when you are first eligible, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty when you do decide to enroll.
While Medicare Part A may be mandatory for some individuals, Medicare Part B is optional. However, it is highly recommended that individuals enroll in Part B when they are first eligible. This is because Part B helps to cover the cost of doctor visits and other outpatient services, and it can provide valuable coverage for individuals who need regular medical care.
There are also certain circumstances in which individuals may be required to enroll in Medicare Part D, which covers prescription drugs. For example, if you have other creditable prescription drug coverage, such as through an employer-sponsored plan, you may be able to delay enrolling in Part D without facing a late enrollment penalty. However, if you do not have creditable coverage and do not enroll in Part D when you are first eligible, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty if you decide to enroll at a later date.
In conclusion, while Medicare coverage is not mandatory, there are certain circumstances in which individuals may be required to enroll in Medicare. It is important to understand the basics of Medicare and how it works in order to make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage. Whether you are automatically enrolled in Medicare or have to enroll on your own, it is important to carefully consider your options and choose the coverage that best meets your needs.
The Importance of Medicare Coverage: Is it Really Mandatory?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program in the United States that provides coverage for individuals who are 65 years old or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. It is a crucial program that ensures access to healthcare for millions of Americans. However, many people wonder if Medicare coverage is mandatory or if they have the option to decline it.
The answer to this question is not a simple yes or no. While Medicare is not technically mandatory, there are certain circumstances in which individuals are required to enroll in the program. For most people, enrolling in Medicare Part A, which covers hospital stays, is automatic and does not require any action. However, individuals who are not automatically enrolled in Part A can still choose to enroll if they meet certain criteria.
Medicare Part B, which covers doctor visits and other outpatient services, does require individuals to actively enroll. If you are eligible for Medicare and do not enroll in Part B when you are first eligible, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty if you decide to enroll later. This penalty can result in higher premiums for as long as you have Medicare.
There are also certain circumstances in which individuals may be required to enroll in Medicare. For example, if you are receiving Social Security benefits, you will be automatically enrolled in Medicare Parts A and B when you turn 65. Similarly, if you are under 65 and have been receiving disability benefits for 24 months, you will be automatically enrolled in Medicare.
It is important to note that while Medicare coverage is not mandatory, it is highly recommended. Medicare provides essential healthcare coverage that can help protect individuals from high medical costs. Without Medicare, individuals may be left without insurance coverage or may have to rely on expensive private insurance options.
Furthermore, Medicare coverage is often more affordable than private insurance options, especially for individuals who are older or have pre-existing conditions. Medicare offers a range of plans with different levels of coverage and costs, allowing individuals to choose the option that best fits their needs and budget.
In addition to the financial benefits, Medicare also provides access to a wide network of healthcare providers. Medicare is widely accepted by doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers across the country, ensuring that individuals have access to the care they need.
In conclusion, while Medicare coverage is not technically mandatory, it is highly recommended for individuals who are eligible. Medicare provides essential healthcare coverage that can protect individuals from high medical costs and ensure access to necessary care. While there are certain circumstances in which individuals may be required to enroll in Medicare, most people have the option to choose whether or not to enroll. However, it is important to carefully consider the benefits of Medicare coverage and the potential consequences of not enrolling before making a decision.
Find Medicare Plans in 3 Easy Steps
We can help get up to $0 monthly premium Medicare plans
Exploring the Legal Requirements of Medicare Coverage
Is Medicare coverage mandatory? This is a question that many people have when it comes to understanding their healthcare options. In this article, we will explore the legal requirements of Medicare coverage and provide you with the information you need to make an informed decision.
Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for individuals who are 65 years of age or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. It is administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and is funded through payroll taxes and premiums paid by beneficiaries.
While Medicare is a widely used program, it is important to note that coverage is not mandatory for everyone. However, there are certain circumstances in which individuals are required to enroll in Medicare or face penalties.
One such circumstance is if you are receiving Social Security benefits. If you are already receiving Social Security benefits when you turn 65, you will be automatically enrolled in Medicare Parts A and B. Part A covers hospital insurance, while Part B covers medical insurance. If you do not wish to be enrolled in Part B, you must actively opt out.
Another circumstance in which Medicare coverage is mandatory is if you are still working and have employer-sponsored health insurance. If you are 65 or older and your employer has 20 or more employees, your employer-sponsored health insurance will be your primary coverage, and Medicare will be secondary. However, if your employer has fewer than 20 employees, Medicare will be your primary coverage, and you must enroll in Parts A and B.
It is important to note that if you do not enroll in Medicare when you are first eligible and do not have other creditable coverage, you may face penalties. The most common penalty is a late enrollment penalty for Part B. This penalty is added to your monthly premium for as long as you have Part B coverage. The penalty amount is based on the number of months you were eligible for Part B but did not enroll.
There are also certain circumstances in which individuals may be eligible for Medicare coverage before the age of 65. For example, individuals with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are eligible for Medicare regardless of their age. In these cases, Medicare coverage is mandatory.
In conclusion, while Medicare coverage is not mandatory for everyone, there are certain circumstances in which enrollment is required. If you are receiving Social Security benefits or have employer-sponsored health insurance, you may be required to enroll in Medicare Parts A and B. Failure to enroll when first eligible may result in penalties. Additionally, individuals with ESRD or ALS are eligible for Medicare coverage regardless of their age. It is important to understand the legal requirements of Medicare coverage and make an informed decision based on your individual circumstances.
Medicare Coverage: Who is Eligible and Why it Matters
Medicare Coverage: Who is Eligible and Why it Matters
Medicare is a federal health insurance program in the United States that provides coverage for individuals who are 65 years old or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. It is a crucial program that ensures access to healthcare for millions of Americans. However, many people wonder if Medicare coverage is mandatory or if they have the option to decline it.
The answer to this question is that Medicare coverage is generally mandatory for individuals who meet the eligibility criteria. If you are 65 years old or older and you or your spouse have paid Medicare taxes for at least 10 years, you are automatically enrolled in Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) when you turn 65. Part A helps cover inpatient care in hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, and hospice care.
While Part A is generally mandatory, you do have the option to decline it if you have other health insurance coverage, such as through an employer or a spouse’s employer. However, it is important to carefully consider this decision, as declining Part A may affect your ability to enroll in other parts of Medicare in the future.
Medicare Part B (medical insurance) is another important component of Medicare coverage. Part B helps cover doctor’s visits, outpatient care, and preventive services. Unlike Part A, Part B is not automatically provided to you when you turn 65. Instead, you have the option to enroll in Part B during your Initial Enrollment Period, which is a seven-month period that begins three months before your 65th birthday.
While Part B is not mandatory, there are penalties for late enrollment. If you do not enroll in Part B during your Initial Enrollment Period and you do not have other creditable coverage, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty for as long as you have Part B. This penalty is added to your monthly premium and can significantly increase your healthcare costs.
In addition to Parts A and B, there are also optional parts of Medicare coverage. Medicare Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, is an alternative to Original Medicare (Parts A and B) that is offered by private insurance companies. Part C plans often include prescription drug coverage and may offer additional benefits, such as dental and vision care.
Medicare Part D is the prescription drug coverage component of Medicare. Part D plans are also offered by private insurance companies and help cover the cost of prescription medications. While Part D is optional, it is important to consider enrolling in a Part D plan if you take prescription medications, as the cost of medications can be significant without coverage.
In conclusion, Medicare coverage is generally mandatory for individuals who meet the eligibility criteria. While Parts A and B are typically automatic, you do have the option to decline Part A if you have other health insurance coverage. However, it is important to carefully consider this decision, as declining Part A may affect your ability to enroll in other parts of Medicare in the future. Part B is not automatic and there are penalties for late enrollment, so it is important to enroll during your Initial Enrollment Period. Parts C and D are optional, but they provide additional coverage that can help reduce healthcare costs. Understanding Medicare coverage and its requirements is essential for ensuring access to necessary healthcare services.
Find Medicare Plans in 3 Easy Steps
We can help get up to $0 monthly premium Medicare plans
The Pros and Cons of Mandatory Medicare Coverage
Is Medicare coverage mandatory? This is a question that many people have when it comes to understanding their healthcare options. Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for individuals who are 65 years of age or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. While Medicare offers a range of benefits, including hospital insurance, medical insurance, and prescription drug coverage, the question of whether or not enrollment is mandatory is an important one to consider.
One of the main advantages of mandatory Medicare coverage is that it ensures that all eligible individuals have access to healthcare. By requiring individuals to enroll in Medicare, the government can ensure that everyone has the opportunity to receive the medical care they need. This is particularly important for older adults who may have limited financial resources and may not be able to afford private health insurance. Mandatory coverage also helps to spread the risk among a larger pool of individuals, which can help to keep costs down for everyone.
Another benefit of mandatory Medicare coverage is that it simplifies the healthcare system. With everyone enrolled in the same program, it becomes easier for healthcare providers to navigate the system and for individuals to understand their benefits. This can help to reduce administrative costs and improve the overall efficiency of the healthcare system. Additionally, mandatory coverage can help to eliminate the confusion and complexity that can come with navigating multiple insurance plans.
However, there are also some drawbacks to mandatory Medicare coverage. One of the main concerns is that it limits individual choice. When enrollment is mandatory, individuals may not have the option to choose a different insurance provider that better suits their needs. This can be particularly problematic for individuals who have specific healthcare needs or who prefer to see certain doctors or specialists. Mandatory coverage can also limit competition among insurance providers, which can lead to higher costs and less innovation in the healthcare industry.
Another potential drawback of mandatory Medicare coverage is that it can place a financial burden on individuals. While Medicare does provide coverage for a range of services, there are still out-of-pocket costs that individuals must pay, such as deductibles and copayments. For some individuals, these costs can be difficult to afford, particularly if they are on a fixed income. Additionally, mandatory coverage means that individuals are required to pay Medicare taxes throughout their working years, which can be a financial burden for some individuals.
In conclusion, while Medicare coverage is not technically mandatory, there are many advantages to enrolling in the program. Mandatory coverage ensures that all eligible individuals have access to healthcare and simplifies the healthcare system. However, there are also drawbacks to consider, such as limited individual choice and potential financial burdens. Ultimately, the decision to enroll in Medicare should be based on an individual’s specific healthcare needs and financial situation. It is important to carefully weigh the pros and cons before making a decision.
Navigating the Different Parts of Medicare: A Mandatory Guide
Is Medicare coverage mandatory? This is a question that many people have when they start to think about their healthcare options. Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for people who are 65 years old or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. While Medicare offers a range of benefits, it is important to understand that not all parts of Medicare are mandatory.
When it comes to Medicare, there are four main parts: Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D. Part A, also known as hospital insurance, is generally considered mandatory. This part of Medicare covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and some home health care services. Most people do not have to pay a premium for Part A if they or their spouse paid Medicare taxes while working.
Part B, on the other hand, is optional. Part B, also known as medical insurance, covers certain doctors’ services, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services. However, there is a monthly premium for Part B, and the cost can vary depending on your income. It is important to note that if you choose not to enroll in Part B when you are first eligible, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty if you decide to enroll later.
Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, is another optional part of Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans are offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare. These plans provide all of the benefits of Part A and Part B, and often include additional benefits such as prescription drug coverage, dental, vision, and hearing services. Medicare Advantage plans may have different costs and rules for how you receive services, so it is important to carefully review the plan options available to you.
Lastly, Part D is the prescription drug coverage part of Medicare. Like Part B, Part D is optional. Part D plans are also offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare. These plans help cover the cost of prescription drugs, and the cost of the plans can vary depending on the drugs covered and the pharmacy network. It is important to review the formulary of each Part D plan to ensure that your medications are covered.
In summary, while Medicare coverage is mandatory for Part A, there are optional parts of Medicare that you can choose to enroll in. Part B, Part C, and Part D all have their own costs and benefits, and it is important to carefully consider your healthcare needs and budget when deciding which parts of Medicare to enroll in. It is also important to note that if you choose not to enroll in certain parts of Medicare when you are first eligible, you may have to pay a penalty if you decide to enroll later. Ultimately, understanding the different parts of Medicare and their requirements can help you navigate the program and make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
Find Medicare Plans in 3 Easy Steps
We can help get up to $0 monthly premium Medicare plans
Medicare Coverage: What Happens if You Don’t Enroll?
Is Medicare coverage mandatory? This is a question that many people approaching the age of 65 ask themselves. Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for individuals who are 65 years old or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. While Medicare coverage is not technically mandatory, there are consequences for not enrolling in the program.
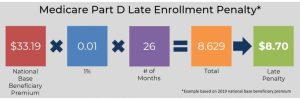
One of the main consequences of not enrolling in Medicare is the potential for late enrollment penalties. If you are eligible for Medicare but choose not to enroll when you first become eligible, you may have to pay a higher premium for Part B, which covers doctor visits and outpatient services. The penalty is calculated by multiplying 10% of the standard premium by the number of full 12-month periods you were eligible for Part B but did not enroll. This penalty is permanent and will be added to your premium for as long as you have Medicare.
Another consequence of not enrolling in Medicare is the potential for gaps in coverage. Medicare provides essential health insurance coverage, including hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs. If you choose not to enroll in Medicare, you will need to find alternative coverage to ensure that you have access to the healthcare services you need. This can be costly and may not provide the same level of coverage as Medicare.
Additionally, not enrolling in Medicare can limit your options for supplemental insurance. Medicare Supplement Insurance, also known as Medigap, is designed to help cover the costs that Medicare does not pay for. However, in order to be eligible for Medigap, you must be enrolled in Medicare Part A and Part B. If you choose not to enroll in Medicare, you will not be able to purchase a Medigap policy, leaving you responsible for paying any out-of-pocket costs that Medicare does not cover.
Furthermore, not enrolling in Medicare can have implications for your future healthcare needs. As you age, your healthcare needs are likely to increase, and having comprehensive insurance coverage becomes even more important. By not enrolling in Medicare, you may be putting yourself at risk of not having adequate coverage when you need it most. This can lead to financial strain and limited access to necessary healthcare services.
In conclusion, while Medicare coverage is not technically mandatory, there are significant consequences for not enrolling in the program. Late enrollment penalties, gaps in coverage, limited options for supplemental insurance, and potential implications for future healthcare needs are all factors to consider when deciding whether or not to enroll in Medicare. It is important to carefully weigh the potential risks and benefits and make an informed decision based on your individual circumstances.
The Financial Implications of Mandatory Medicare Coverage
Is Medicare coverage mandatory? This is a question that many individuals approaching retirement age may ask themselves. Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for individuals who are 65 years or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. While Medicare offers a range of benefits, including hospital insurance (Part A), medical insurance (Part B), and prescription drug coverage (Part D), it is important to understand the financial implications of mandatory Medicare coverage.
One of the key aspects to consider when it comes to Medicare coverage is the cost. Medicare is not free, and individuals are required to pay premiums, deductibles, and co-payments for certain services. The cost of Medicare can vary depending on the specific coverage options chosen, as well as an individual’s income level. For example, higher-income individuals may be subject to higher premiums for Medicare Part B and Part D. It is important to carefully review the costs associated with Medicare coverage to ensure that it fits within your budget.
Another financial consideration is the potential impact on other health insurance coverage. For individuals who are still working and have employer-sponsored health insurance, it is important to understand how Medicare will interact with this coverage. In some cases, individuals may be required to enroll in Medicare once they become eligible, even if they have other health insurance. This can result in duplicate coverage and potentially higher costs. It is important to carefully review the terms of your employer-sponsored health insurance plan to understand how it will coordinate with Medicare.
In addition to the cost of Medicare coverage, it is also important to consider the potential limitations of the program. While Medicare provides coverage for a wide range of medical services, it does not cover everything. For example, Medicare does not cover long-term care, dental care, or vision care. This means that individuals may need to consider additional insurance options or out-of-pocket expenses to cover these services. It is important to carefully review the coverage limitations of Medicare to ensure that you have adequate coverage for your specific healthcare needs.
One potential option to consider when it comes to Medicare coverage is Medicare Advantage plans. These plans, also known as Medicare Part C, are offered by private insurance companies and provide an alternative to traditional Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans often offer additional benefits, such as prescription drug coverage and dental and vision care. However, it is important to carefully review the costs and coverage limitations of these plans to ensure that they meet your specific healthcare needs.
In conclusion, while Medicare coverage is not mandatory, it is an important consideration for individuals approaching retirement age. Understanding the financial implications of Medicare coverage is crucial in order to make informed decisions about your healthcare. The cost of Medicare, potential impact on other health insurance coverage, and limitations of the program are all factors that should be carefully considered. Additionally, exploring alternative options such as Medicare Advantage plans can provide additional coverage options. By carefully reviewing your healthcare needs and the financial implications of Medicare coverage, you can make the best decision for your individual situation.
Find Medicare Plans in 3 Easy Steps
We can help get up to $0 monthly premium Medicare plans
Medicare Coverage: How it Affects Your Healthcare Options
Is Medicare coverage mandatory? This is a question that many people have when it comes to their healthcare options. Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for individuals who are 65 years of age or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. While Medicare offers a range of benefits and can be a valuable resource for many individuals, it is not mandatory for everyone.
Medicare is divided into several parts, each covering different aspects of healthcare. Part A covers hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, and some home health services. Part B covers doctor visits, outpatient care, and medical supplies. Part D covers prescription drugs. And finally, Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, is an alternative to traditional Medicare that offers additional benefits through private insurance companies.
For individuals who are eligible for Medicare, enrolling in Part A is generally automatic. This means that if you or your spouse have paid Medicare taxes while working, you will be enrolled in Part A when you turn 65. However, enrolling in Part B is not automatic and requires individuals to sign up during their Initial Enrollment Period, which is a seven-month period that begins three months before the month you turn 65.
While enrolling in Medicare is not mandatory, there are certain situations where it may be beneficial or even necessary. For example, if you are currently covered by an employer-sponsored health insurance plan, you may choose to delay enrolling in Medicare Part B. However, it is important to note that if you do not enroll in Part B when you are first eligible and do not have other creditable coverage, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty when you do decide to enroll.
Additionally, if you are eligible for Medicare and choose not to enroll, you may face gaps in your healthcare coverage. Medicare provides comprehensive coverage for a wide range of healthcare services, and without it, you may be responsible for paying for these services out of pocket. This can be particularly costly for individuals who require frequent medical care or have chronic health conditions.
It is also worth noting that while Medicare provides coverage for many healthcare services, it does not cover everything. For example, Medicare does not cover long-term care, dental care, or vision care. If you require these services, you may need to explore other options, such as purchasing supplemental insurance or paying for these services out of pocket.
In conclusion, while Medicare coverage is not mandatory for everyone, it is an important healthcare option to consider. Medicare provides comprehensive coverage for a wide range of healthcare services and can be a valuable resource for individuals who are 65 years of age or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. However, it is important to carefully consider your individual circumstances and healthcare needs before making a decision about enrolling in Medicare.
Demystifying the Myths: Debunking Misconceptions about Mandatory Medicare Coverage
Is Medicare coverage mandatory? This is a question that many people have when it comes to understanding their healthcare options. There are a lot of misconceptions out there about whether or not Medicare coverage is required, and it’s important to separate fact from fiction. In this article, we will demystify the myths and debunk the misconceptions about mandatory Medicare coverage.
First and foremost, it’s important to understand what Medicare is. Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for people who are 65 years old or older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. It is divided into different parts, including Part A, which covers hospital stays, and Part B, which covers doctor visits and other outpatient services. There is also Part C, which is known as Medicare Advantage, and Part D, which covers prescription drugs.
Now, let’s address the myth that Medicare coverage is mandatory. The truth is that while most people are eligible for Medicare when they turn 65, enrollment is not automatic. In fact, if you are already receiving Social Security benefits, you will be automatically enrolled in Medicare Parts A and B when you turn 65. However, if you are not receiving Social Security benefits, you will need to actively enroll in Medicare during your Initial Enrollment Period, which begins three months before your 65th birthday and ends three months after.
Another misconception is that you must enroll in Medicare when you turn 65, even if you have other health insurance coverage. This is not true. If you are still working and have employer-sponsored health insurance, you may choose to delay enrolling in Medicare without facing any penalties. However, it’s important to note that once you retire or lose your employer-sponsored coverage, you will have a Special Enrollment Period to sign up for Medicare without penalties.
It’s also worth mentioning that while Medicare coverage is not mandatory, there are certain circumstances where it may be beneficial to enroll. For example, if you have limited income and resources, you may qualify for assistance programs that can help cover the costs of Medicare premiums and other healthcare expenses. Additionally, if you choose not to enroll in Medicare when you are first eligible and later decide to do so, you may face late enrollment penalties in the form of higher premiums.
In conclusion, Medicare coverage is not mandatory, but it is available to most individuals who are 65 years old or older. While enrollment is not automatic, it is important to understand your options and make an informed decision about whether or not to enroll in Medicare. If you have other health insurance coverage, you may choose to delay enrollment without penalties. However, it’s important to consider your individual circumstances and weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks of Medicare coverage. Ultimately, the choice is yours, but it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or Medicare expert to ensure that you are making the best decision for your healthcare needs.
Find Medicare Plans in 3 Easy Steps
We can help get up to $0 monthly premium Medicare plans
Conclusion
Medicare coverage is not mandatory for all individuals. However, it is mandatory for certain groups of people, such as those who are 65 years or older and eligible for Social Security benefits. Additionally, individuals with certain disabilities may also be required to enroll in Medicare.